Appearance
课程项目二:复数运算
项目需求
程序简介
程序编译及运行环境
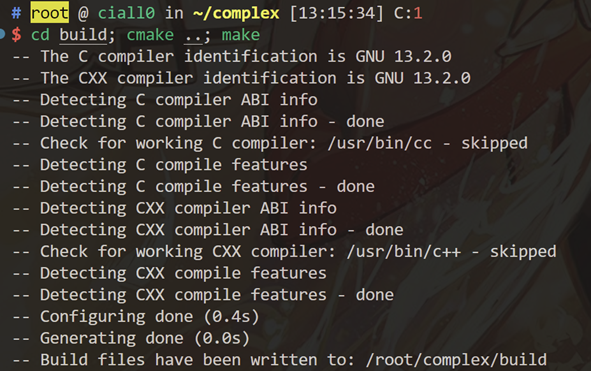
编译命令:
$ cwd = ${fileDir}
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make 生成文件在项目根目录下,命名为Complex
Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
cmake version 3.28.3
gcc (Ubuntu 13.2.0-23ubuntu4) 13.2.0
程序特点
支持变量的连续的加减乘除;支持变量与数的混合运算与括号解析;支持对复杂合表达式的运算;支持任意长度的大数加减乘运算;支持自增、自减、+=等符号操作;有部分的错误输入提示。
程序功能展示
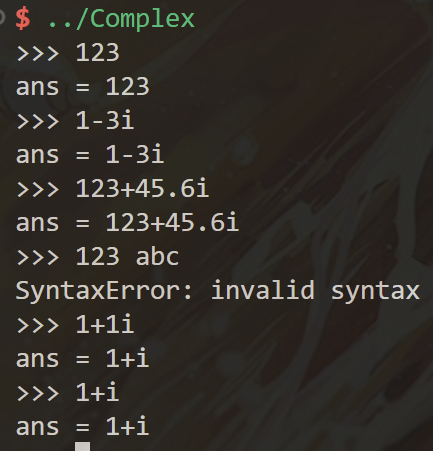
- 基本的加减乘除运算
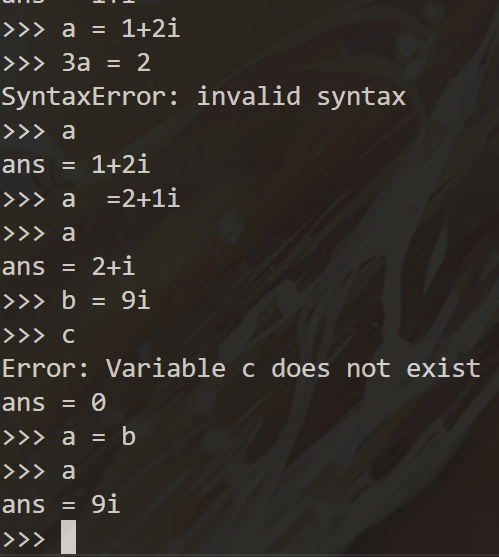
- 赋值操作
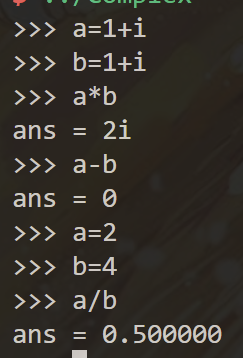
- 变量间的加减乘除
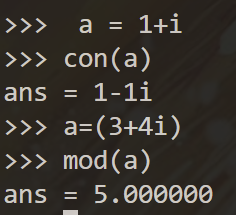
- 模运算和共轭
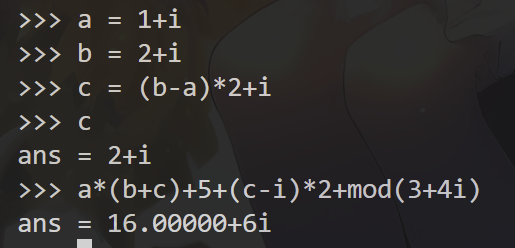
- 复杂运算
- 大数运算


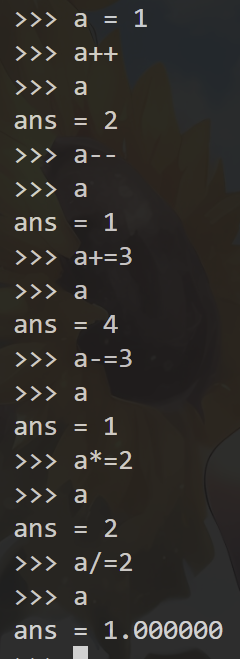
- 自增、自减运算符与+=等运算符
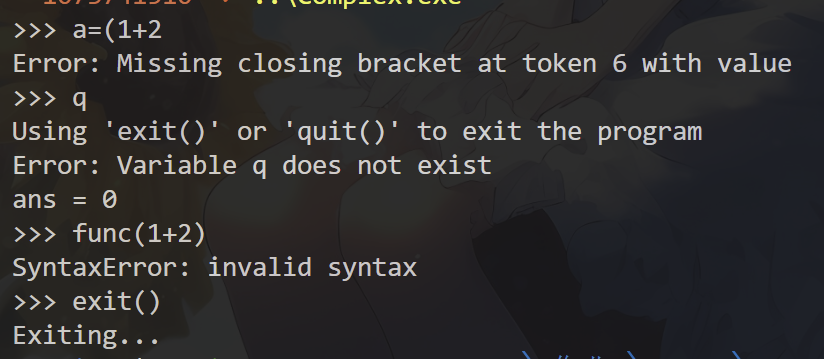
- 错误处理

程序实现与设计思路
数学运算的实现
使用上一次乘法项目的代码,把所有数据视为字符串存储,并实现字符串的加、减、乘,对于除法,则使用long double进行计算
cpp
//mul.h
//高精度加法
std::string addStrings(const std::string &num1, const std::string &num2);
//高精度减法
std::string subtractStrings(const std::string &num1, const std::string &num2);
std::string stringMultiple(const std::string &num1, const std::string &num2);
std::string stringDivide(const std::string &num1, const std::string &num2);
std::string stringPow(const std::string &num1, const std::string &num2);
std::string stringSqrt(const std::string &num1, const std::string &num2);复数类的实现
将程序中将所有的数据都使用字符串存储到complexObject对象中,并重载各种运算符,定义
cpp
//complexObject.h
class complexObject {
public:
string real;
string virt;
string res;
complexObject(string real, string virt) : real(real), virt(virt) {}
complexObject(string str);
complexObject() : real("0"), virt("0") {}
void operator=(const complexObject &c);
string getRes();
complexObject operator+(const complexObject &c);
complexObject operator-(const complexObject &c);
complexObject operator*(const complexObject &c);
complexObject operator/(const complexObject &c);
complexObject operator%(const complexObject &c);
complexObject operator^(const complexObject &c);
void operator--(int);
void operator++(int);
complexObject operator+=(const complexObject &c);
complexObject operator-=(const complexObject &c);
void operator*=(const complexObject &c);
void operator/=(const complexObject &c);
friend complexObject con(complexObject &c1);
friend complexObject mod(complexObject &c1);
};REPL的实现
预处理,使用Lexer类,利用正则匹配将输入分片
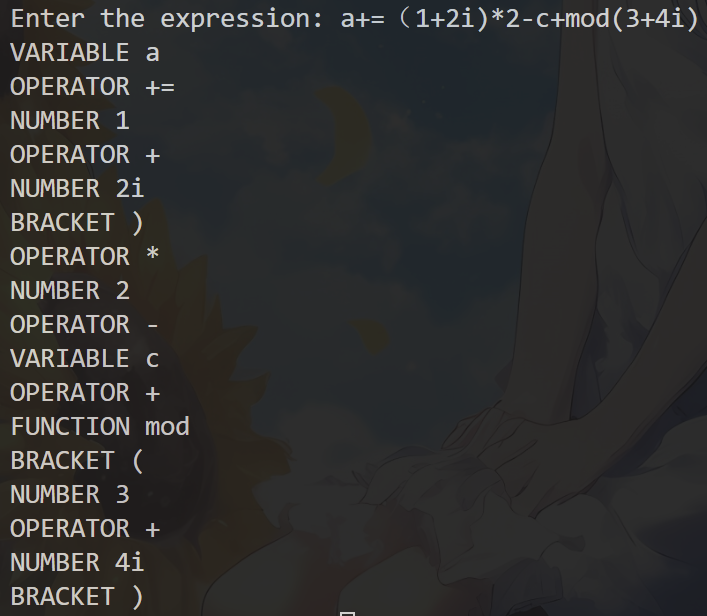
- 经过处理后输入会被分隔并分类为变量
VARIABLE、运算符BRACKET、数字NUMBER、括号BRACKET与函数FUNCTION五种tokens。
- 经过处理后输入会被分隔并分类为变量
构建AST树
cpp
struct ASTNode {
// 构建AST
struct ASTNode {
string type;// 节点类型
string value;// 节点值
vector<ASTNode*> children;
};
class AST : public Lexer {
private:
size_t pos;
public:
ASTNode* root;
vector<Token> tokens;
AST(string strs) : Lexer(strs), pos(0) {
tokens = tokenize();
}
AST() : Lexer(""), pos(0) {}
AST& operator=(const AST& ast) {
if (this == &ast) {
return *this;
}
root = ast.root;
tokens = ast.tokens;
pos = 0;
return *this;
}
void buildAST();// 构建AST
ASTNode* parseExpression();
ASTNode* parseTerm();
ASTNode* parseFactor();
ASTNode* parseValue();
ASTNode* parseFunction();
void printAST(ASTNode* node, int depth);
void printLex();
void checkAST(ASTNode* node);
};- 通过AST.buildAST()函数可以构建节点为ASTNode的简易语法树, 构建的语法树根据有无等号将根节点的类型分为ASSIGNMENT和EXPRESSION类型,然后根据括号->函数->乘除->加减的顺序解析tokens,并且在解析的过程中与解析完成后判断输入语法是否正确。
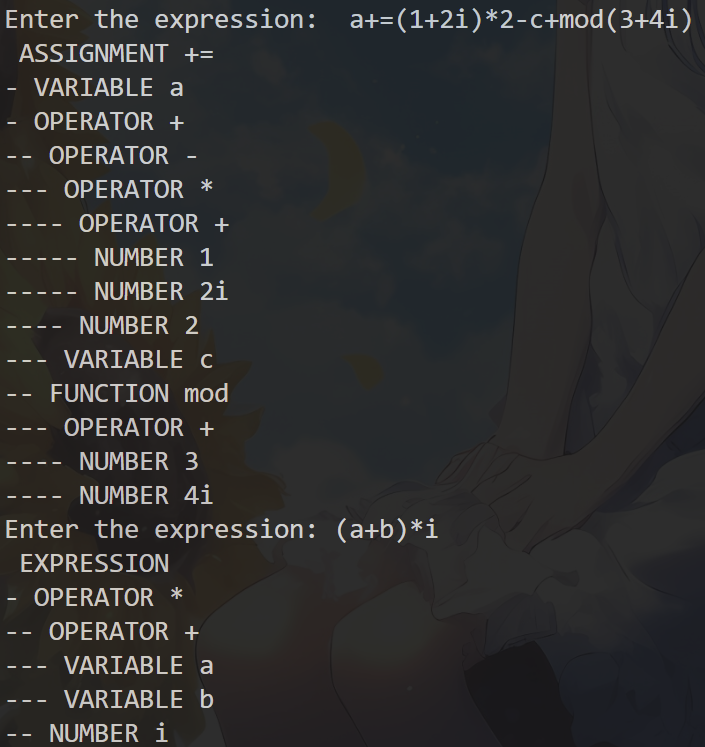
- 通过AST.buildAST()函数可以构建节点为ASTNode的简易语法树, 构建的语法树根据有无等号将根节点的类型分为ASSIGNMENT和EXPRESSION类型,然后根据括号->函数->乘除->加减的顺序解析tokens,并且在解析的过程中与解析完成后判断输入语法是否正确。
AST树的解析与主循环的实现
cpp
class Parser {
public:
Parser() {};
void mainloop();
string input;
unordered_map<string, complexObject> variablesList;
vector<string> __builtin__type = {"i", "e", "con", "mod"};
void checkexit();
void checkvariablename();
void parseAssignment();
complexObject parseTerm();
complexObject parseExpression();
complexObject parseFactor();
complexObject parseFunction(ASTNode* node);
complexObject parseValue();
complexObject evaluateNode(ASTNode* node);
void ckeckVariableExist();
void parse();
void showVariables();
AST ast;
size_t pos;
ASTNode* &root = ast.root;
};
void Parser::mainloop()
{
while(true) {
cout << ">>> ";
getline(cin, input);
checkexit();
try {
//showVariables();
ast = AST(input); // 重新初始化AST对象
root = nullptr; // 重置root指针
//ast.printLex();
ast.buildAST();
ast.checkAST(ast.root);
root = ast.root;
checkvariablename();// 检查变量名是否合法
//ast.printAST(ast.root, 0);
parse();
} catch (const std::runtime_error &e) {
cout << e.what() << endl;
continue;
}
}
}- 使用Parser.variableList存储运行时的变量,在每次使用getlline获取输入后构建一个对应的AST对象,通过checkAST与checkvariblename再次检查输入是否合法,然后再通过Parser.parse()解析并执行
cpp
void Parser::parse()
{
// 解析ASSIGMENT类型
if (root->type == "ASSIGNMENT" && root->value == "=") {
string varname = root->children[0]->value;
complexObject value = evaluateNode(root->children[1]);
variablesList[varname] = value;
}
else if (root->type == "ASSIGNMENT" && (root->value == "++" || root->value == "--")) {
string varname = root->children[0]->value;
if (variablesList.find(varname) == variablesList.end()) {
throw runtime_error("Error: Variable " + varname + " does not exist");
}
if (root->value == "++") {
complexObject value = variablesList[varname];
value++;
variablesList[varname] = value;
return;
} else {
complexObject value = variablesList[varname];
value--;
variablesList[varname] = value;
return;
}
}
else if (root->type == "ASSIGNMENT" && (root->value == "+=" )) {
variablesList[root->children[0]->value] += evaluateNode(root->children[1]);
}
else if (root->type == "ASSIGNMENT" && (root->value == "-=" )) {
variablesList[root->children[0]->value] -= evaluateNode(root->children[1]);
}
else if (root->type == "ASSIGNMENT" && (root->value == "*=" )) {
variablesList[root->children[0]->value] *= evaluateNode(root->children[1]);
}
else if (root->type == "ASSIGNMENT" && (root->value == "/=" )) {
variablesList[root->children[0]->value] /= evaluateNode(root->children[1]);
}
// 解析EXPRESSION类型
else if (root->type == "EXPRESSION") {
complexObject res = parseExpression();
cout << "ans = " << res.getRes() << endl;
}
}遇到的问题与解决方法
主要集中在用户输入的解析与处理方面上。
由于REPL环境要处理的输入较为复杂,之前也未深入了解抽象语法树,故在这方面上碰了不少壁,也浪费了较多时间在编写与调试方面上。
耗费时间最多的在排查在输入a++后再次输入a会导致程序出现错误的问题上:
cpp
while(true){
string text;
cout << "Enter the expression: ";
getline(cin, text);
try {
AST ast(text);
//ast.printLex();
ast.buildAST();
ast.checkAST(ast.root);
ast.printAST(ast.root, 0);
//cout << endl;
} catch (const std::runtime_error &e) {
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
}如在这段代码中(ast/test.cpp),每一次循环会重新初始化一个AST对象,但是在第一次输入a++后第二次输入a却会导致在basic_string.h的6249行处出现字段错误,即一个已经销毁的对象影响了一个新生成的对象: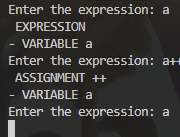
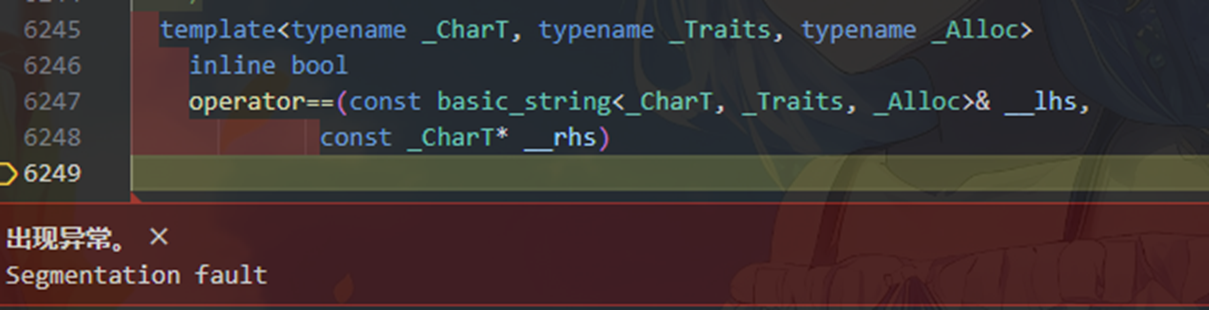
最后仍旧没有找引发错误的所在,解决办法是在ast.cpp的52-62行,重复添加了对只有一个变量的EXPRESSION表达式的判断与构建。
cpp
///
if (tokens.size()==1 && tokens[0].type == "VARIABLE")
{
root->type = "EXPRESSION";
ASTNode* variableNode = new ASTNode();
variableNode->type = "VARIABLE";
variableNode->value = tokens[0].value;
root->children.push_back(variableNode);
return;
}
///项目总结
程序目前仍是一较不完善的半成品,如对一些输入仍然无法正确解析与计算,还不支持科学计数法与用户自定义输出等。在此次项目中,对REPL环境的以及抽象语法树的实现有了一定了解,认识到了完善的错误处理机制能够程序健壮性的提升以及可以更好地在调试中排查与定位数据。