Appearance
GGH公钥加密方案
方案介绍
- 注:该方案已于1999年被Ngugen破解,现已不安全。
- 密钥生成:选择一个优质基
作为私钥。选择一个整数矩阵 ,使得 。计算公钥 ,得到劣质基 作为公钥。 - 加密:
。消息为小向量 ,选择噪声 ,输入公钥 ,计算密文 。 - 解密:
。调用Babai算法,输入私钥 ,计算 ,因为:
- 二维格上的演示:
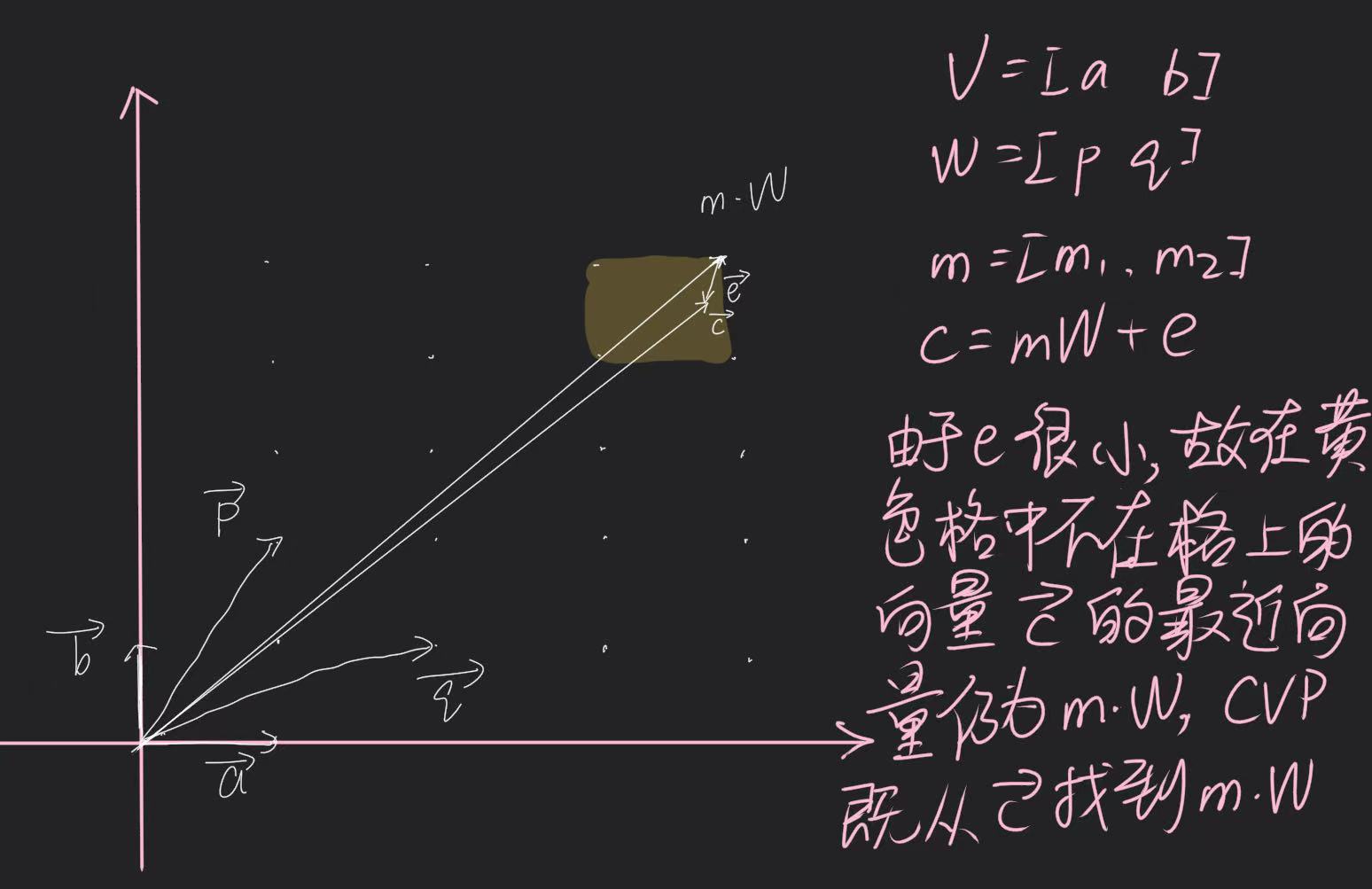
- 由于在Babai算法中,噪声r是小向量,则求出的矩阵T是小的,四舍五入后就为0,所以
代码举例
ps: 中文区这方面的资料是真的少
- 生成优质基
python
#type: ignore
# sage
def hadamard_ratio(V):
prod_norm = 1
n = V.nrows()
for i in range(n):
row = V.row(i)
row_norm = row.norm() # 计算欧几里得氏范数
prod_norm *= row_norm
# 计算 Hadamard 比率
ratio = abs(V.determinant()) / prod_norm if prod_norm != 0 else 0
return (ratio)**(1/n).n()
def gen_good_basis(m,q,h):
"""
## 生成优质基,满足Hadamard比率大于h
- m: 基的维度
- q: 随机矩阵的元素范围[-q,q]
- h: Hadamard比率的下限
"""
A = random_matrix(ZZ,m,m,x=-q,y=q)
while hadamard_ratio(A) < h:
A = random_matrix(ZZ,m,m,x=-q,y=q)
return A
m = 5
V = gen_good_basis(m,1000,0.9)
print(V)
print(hadamard_ratio(V))[ 231 715 266 -815 -69]
[ 41 -228 -773 -123 -510]
[ -58 509 -56 569 -217]
[ 646 -491 -293 -106 279]
[ 96 -984 695 -500 -991]
0.908206075850296- 生成随机矩阵
,且
python
# type: ignore
def random_SLnZ(n, minval=-10, maxval=10):
"""
## 生成一个n阶行列式为正负1的矩阵
- n: 矩阵的阶数
- minval: 随机数的最小值
- maxval: 随机数的最大值
"""
while True:
M = random_matrix(ZZ, n, n, x=minval, y=maxval)
d = M.determinant()
if d != 0:
# 用伴随矩阵调整为行列式1
M = M * d**(-1)
M = M.change_ring(QQ)
if M.determinant() == 1 or M.determinant() == -1:
return M
# 生成一个5阶行列式为1的矩阵
U = random_SLnZ(5)
print(U)
print(U.determinant())[-6 1 -7 -1 8]
[-7 -8 -3 -4 9]
[-4 -2 -1 -3 2]
[ 2 8 -5 7 -7]
[ 7 -7 8 -2 10]
1- 生成劣质基
作为公钥,Hadamard比率很小
python
#type: ignore
W=U*V
print(W)
print(hadamard_ratio(W))[ -817 -15462 3876 -3110 -6784]
[ -3491 -11600 11917 906 -4821]
[ -2694 -3408 2807 2255 -1306]
[ 4930 512 -12288 -2701 5757]
[ 534 1815 14361 -5080 -9117]
0.0702745725647819- 加密
,噪声 。
python
#type: ignore
message=Matrix([-78,48,5,66,89])
r=Matrix([-9,-5,1,-2,4])
c = message*W+r
print(c)[ 255585 827518 750845 -333045 -140233]
- 解密
python
A=((c*V.inverse()).n()).apply_map(lambda x: round(x))
print(A)
V_1 = A*V
print(V_1)
decrypt = V_1*W.inverse()
print("Dec=")
print(decrypt)
print((c-V_1).norm()) # 计算解密后的向量的范数
[ 255585 827518 750845 -333045 -140233]
[ 867 -567 779 155 246]
[ 255594 827523 750844 -333043 -140237]
Dec=
[-78 48 5 66 89]
11.269427669584646可以看到,解密后的消息和Message一致。
最后再看看使用劣质基,既公钥解密的情况
python
A=((c*W.inverse()).n()).apply_map(lambda x: round(x))
print(A)
V_1 = A*V
print(V_1)
decrypt = V_1*W.inverse()
print("Dec=")
print(decrypt)
print((c-V_1).norm())[-64 53 -93 21 62]
[ 12301 -176500 -15848 -40502 -58016]
Dec=
[-9225 -3168 67166 30934 18458]
1321891.9952730632- 可以看到解密后的消息和message完全不同,二者和原向量的欧几里得范数的差距也较大,因此,对于劣质基,Babai算法的结果无法作为CVP的解。
- PS:生成公私钥这步操作由于纯靠随机数碰运气试,耗时挺不稳定的,但是平均都要1s往上,目前还不清楚在实际应用中是如何处理的。